1.5. Port Scanning & Server Security #
Ports #
A port is used in TCP and UDP connections to direct network traffic to a specific service.
Ports come in many different categories:
- Well known ports (0 - 1023)
- Registered ports (1024 - 49151)
- Dynamic/private ports (49152 - 65535)
- Standard services:
- TCP 80: HTTP
- TCP 443: HTTPS
- TCP 22: SSH
- TCP 23: Telnet
- TCP 25: SMTP
- TCP/UDP 53: DNS
- UDP 161: SNMP
- TCP 179: BGP
TCP Connections #
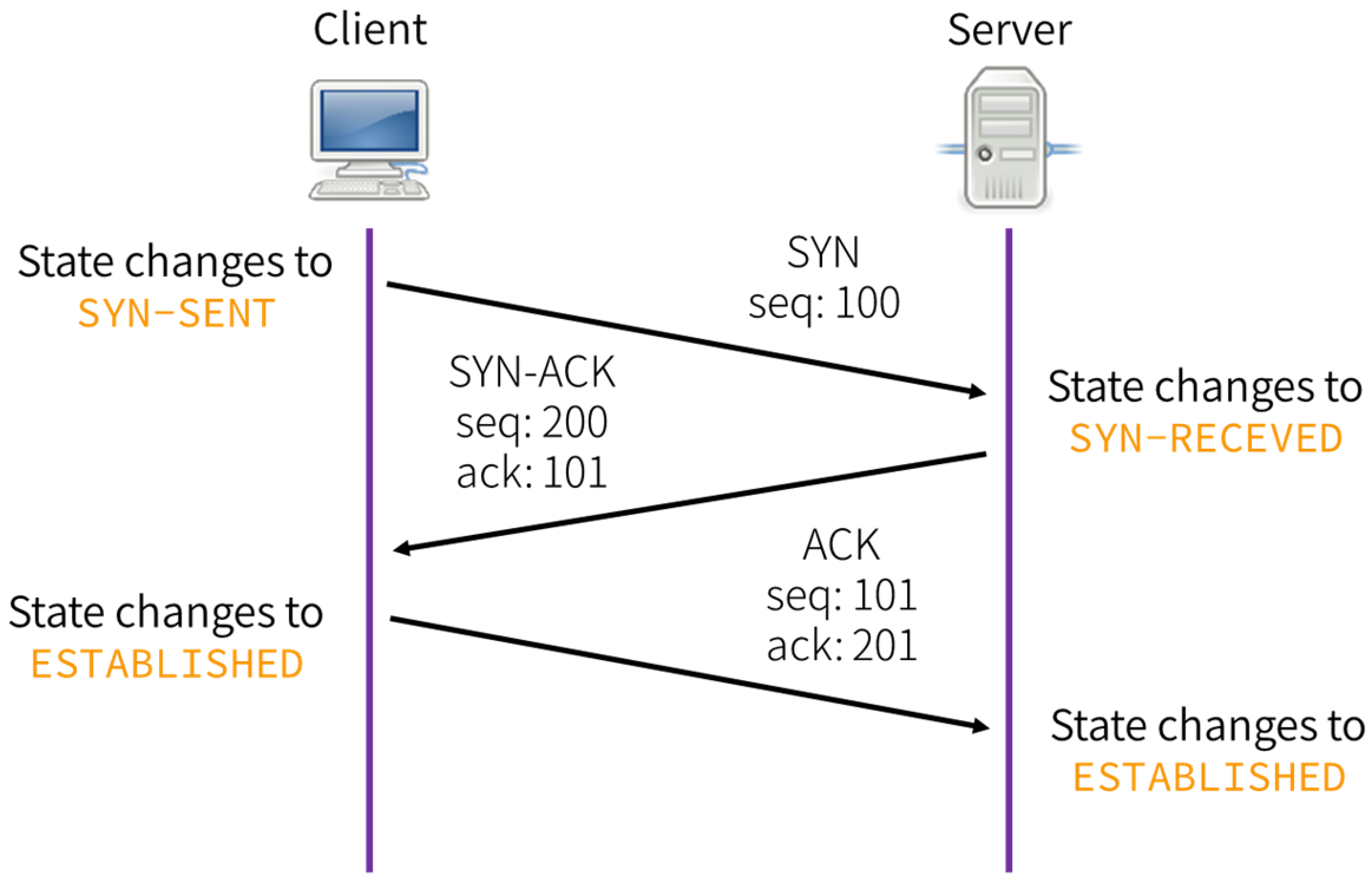
TCP Connections are documented in RFC 793.
The client sends a SYN to the server, the server responds with SYN-ACK, then the client finalises the connnection by responding with ACK.
UDP Connections #
UDP Connections are documented in RFC 768.
Unlike TCP, UDP does not have an explicit handshake sequence.
Port Scanning #
Port scanning is the act of sending packets systematically to a system in order to determine what ports are open, and hence what services are running.
TCP Scanning #
TCP Scanning can tell you more information than UDP scanning due to the TCP handshake. The table below shows what each reply could mean.
| Message Sent | Reply from Server | Determined to be… |
|---|---|---|
| SYN | SYN/ACK | Open (listening) |
| SYN | RST | Closed |
| ACK | RST | Open (with RST SN set according to ACK ISN) |
| ACK | RST | Closed (SN=0) |
| FIN | Nothing | Open |
| FIN | RST | Closed (or open if Windows machine) |
| Anything else | Nothing | Open |
| Anything else | RST | Closed |
UDP Scanning #
Due to the send-and-forget nature of UDP, UDP scanning takes much longer and is less reliable than TCP scanning.
| Message Sent | Reply from Server | Determined to be… |
|---|---|---|
| UDP | Nothing | Open (listening) |
| UDP | ICMP Port Unreachable | Closed |
Nmap #
Nmap is a command-line utility used for port scanning.
Specifying Host #
Nmap supports multiple formats for specifying a target.
- IP address/mask (
192.168.0.0/24) - Ranges (
192.168.0.1-200) - Wildcards (
192.168.0.*) - Subnet masks can be 0-32
/32: Scans the single host/24: Scan Class C address/16: Scan Class B address/8: Scan Class A address/0: Scans the whole internet
Scan Types #
Nmap allows you to scan using different methods:
- Connect
- Basic form of TCP scanning
- Opens a connection to every specified port on the machine
- SYN Stealth
- Also known as half-open scanning, since it doesn’t fully open a TCP connection
- Sends a SYN packet, and wait for an ACK
- FIN Stealth
- Sends a FIN packet (ending transmission)
- Ignored if service is running
- Receives RST if service isn’t running
OS Hardening #
By default, an operating system may not be very secure.
OS hardening is the act of securing an operating system by:
- Applying all the security patches
- Removing all unnecessary services, closing all unneeded ports, and removing any unneeded protocols
- Enforcing file and directory permission policies
- Designing the authorisation procedure thoroughly
Security Monitoring Programs #
Software can be installed to monitor the security of a network and systems on it.
- Host Intrusion Detection
- Checks the log files in order to trace intrusions
- System Integrity Checkers
- Creates a hash of the system and compares against the baseline to notice modifications
- Alerts administrator of immediate change
- Personal Firewalls
- Filters incoming and outgoing packets
- Determines what ports need to be open
- Keeps a log of network traffic, and firewall events
Server Security #
Servers contain sensitive information that is critical to the operation of a business.
Each service running on the server should be hardened to reduce the risk of intrusion and downtime.
- Web servers
- Delete sample scripts
- Remove headers containing server version
- Know what happens in a failure
- Databases
- Isolate production database
- Strong security
- Hide location from public