1.8. Network Traffic Analysis #
Common Headers #
Below are the common headers you will see when analysing packets.
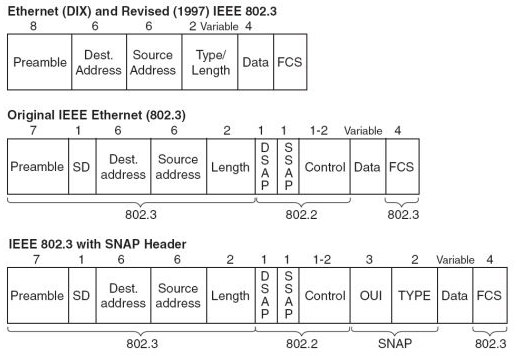
Ethernet Frame #
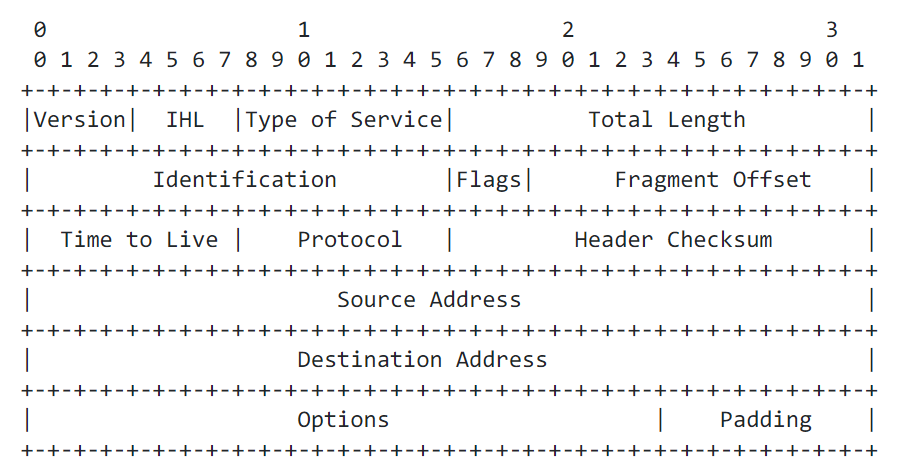
IPv4 Header #
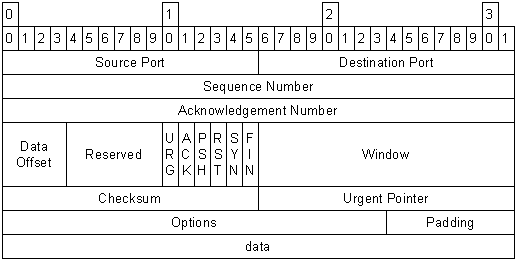
TCP Header #
Network Devices #
Switch #
A switch is a device which forwards network traffic based on its MAC address, hence they typically operate at Layer 2 (Data Link).
Switches use the spanning tree protocol to prevent looping within the network.
A managed switch makes use of SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). This allows:
- Monitoring of the device and port health
- Configuration of port bandwidth
- Use of a VPN
For traffic monitoring, port mirrors are needed.
Router #
A router is similar to a switch, except it stores then forwards based on the Layer 3 (Network) header. IP is a Layer 3 protocol.
A router usually supports the following features:
- Queuing techniques
- Buffer management
- Different scopes: core, provider-edge, customer-edge
- Uses (e)BGP, iBGP, OSPF
- May implement MPLS
- Management via SNMP
- Management information using IPFIX/netFlow and sFlow
Autonomous Systems #
Autonomous Systems are large networks that work together to make up the internet. Each AS has a unified routing policy.
Every device on the internet is connected to an AS.
Each AS broadcasts the IP addresses it manages to other ASes using BGP.
Every AS is assigned a unique AS Number.