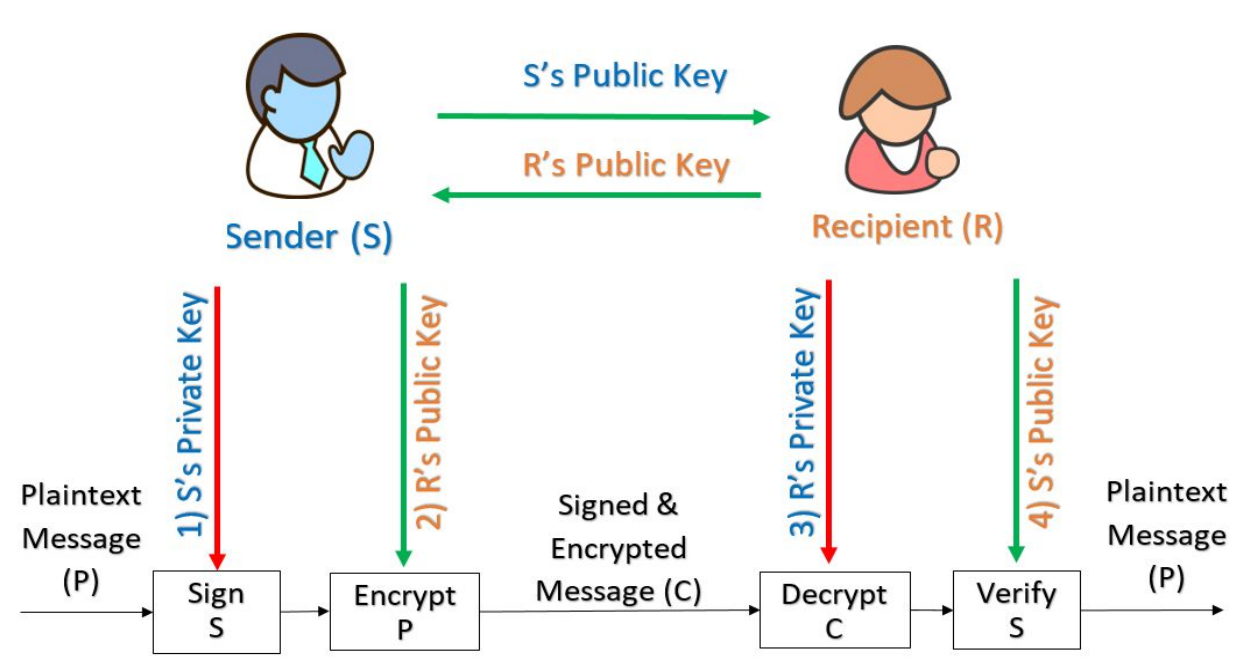
1.11. CIA and Cryptography #
CIA is an abbreviation for confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
- Confidentiality: Protecting the information from disclosure to unauthorised users
- Integrity: Protecting the information from being modified by unauthorised parties
- Availability: Ensures that authorised users are able to access the information when needed
AAA Security Model #
- Authentication: Verifies a user is who they say they are
- Authorisation: Gives a user their legitimate access rights and prevents access to other resources
- Accounting: Ensures that user activies can be traced back to them
Cryptography Process #
- Plaintext: The readable data which is used by the cryptographic process
- Ciphertext: The un-readable data which is the output of the cryptographic process
- Encryption: The process of turning plaintext into ciphertext
- Decryption: The process of turning ciphertext into plaintext
- Cryptanalysis: Used by an interceptor of the ciphertext to determine the plaintext information
Cryptographic Techniques #
Simplest arrangements rely on security of the cryptographic algorithm.
Security can be improved by using a key:
- Constant algorithm, but produces a different output depending on the key
- Key can be changed
- Number of possible keys is known as the key space
- Key distribution could be a problem
Substitution #
- Symbols in the plaintext are replaced with different symbols in the ciphertext.
- Systematic replacement of one symbol by another (monoalphabetic).
- Uses a lookup table, for example, Caesar Cipher
- Vulnerable to statistical analysis, for example, based upon the frequency of character occurrence
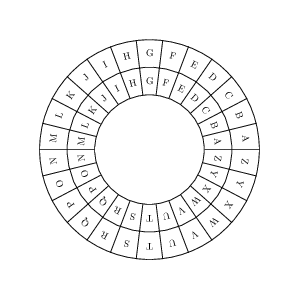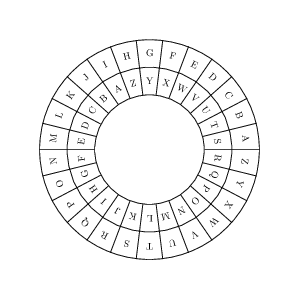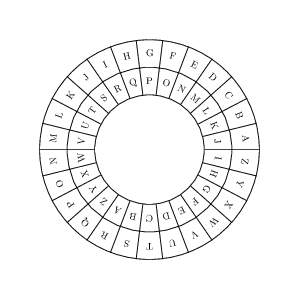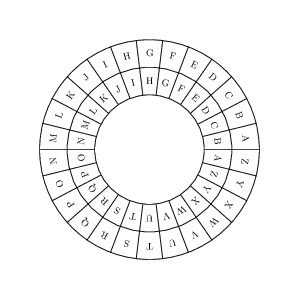
Cryptanalysis of Substitution Ciphers #
- Spaces in ciphertext give sentence structure
- Subtitute small words in ciphertext
- Guess repeated characters
- Apply logic to the rest of the message
- Easy to break based on the rules of English
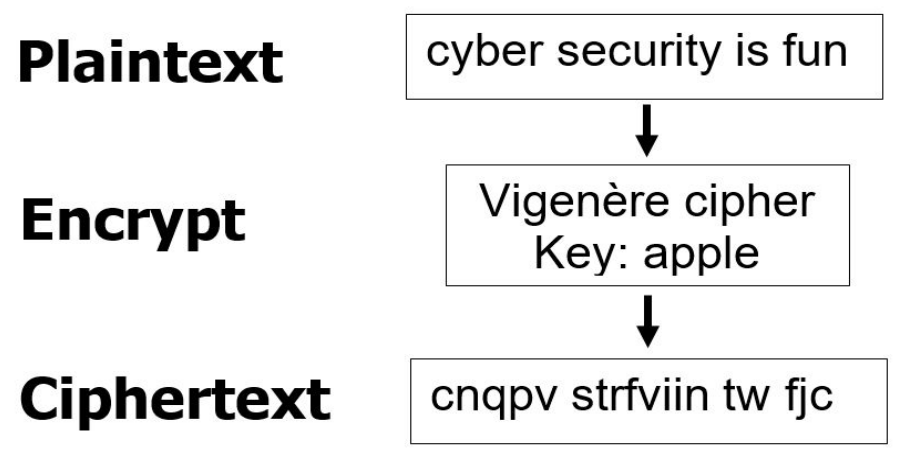
Polyalphabetic Substituion #
Multiple subtitution alphabets are used.
Example: Vigenère Cipher and the Enigma machine.
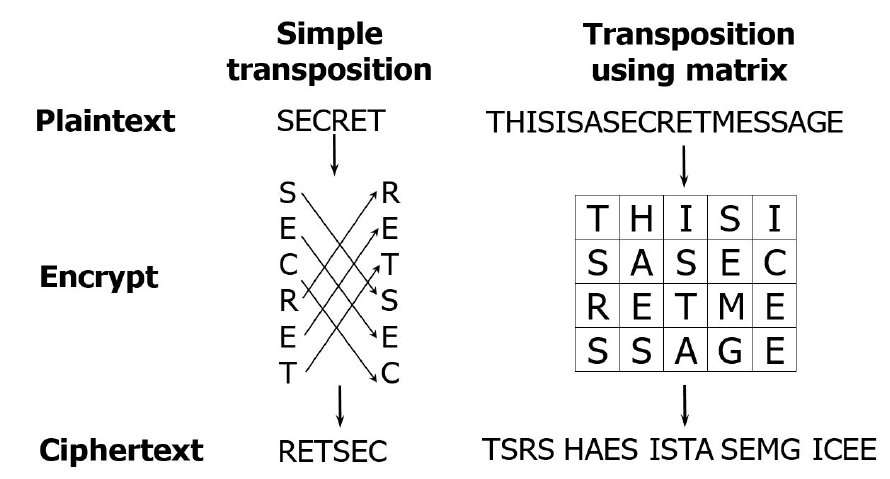
Transposition #
Symbols in the plaintext are moved into different positions in the ciphertext.
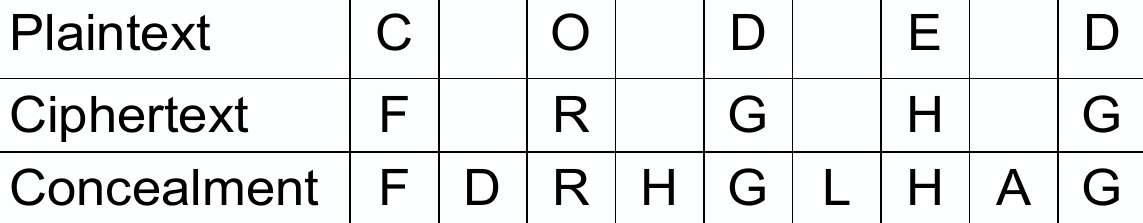
Concealment #
Additional symbols are placed in the ciphertext to conceal the context.
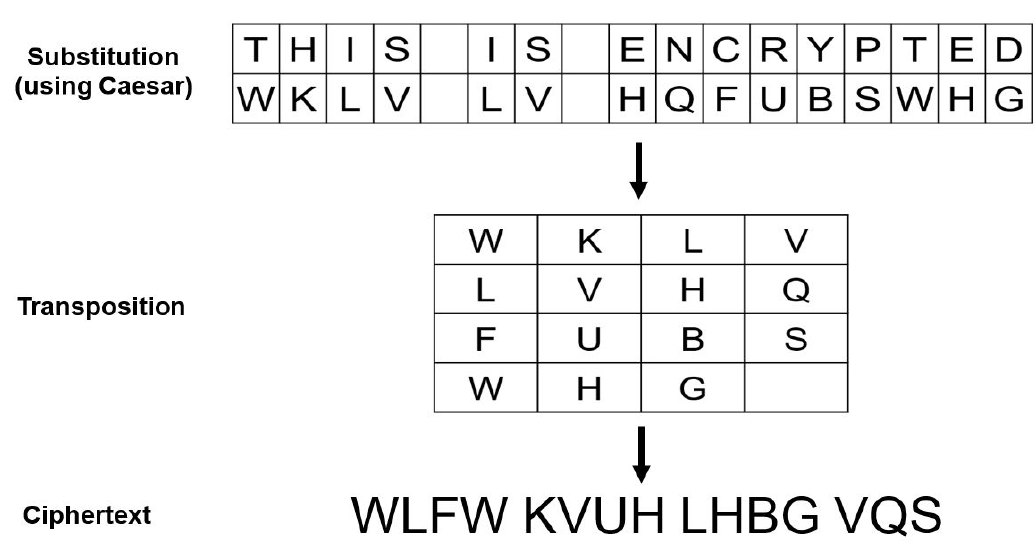
Product Ciphers #
Combines two or more basic methods, offering better security.
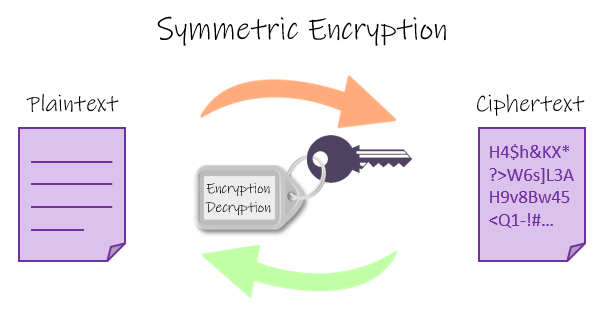
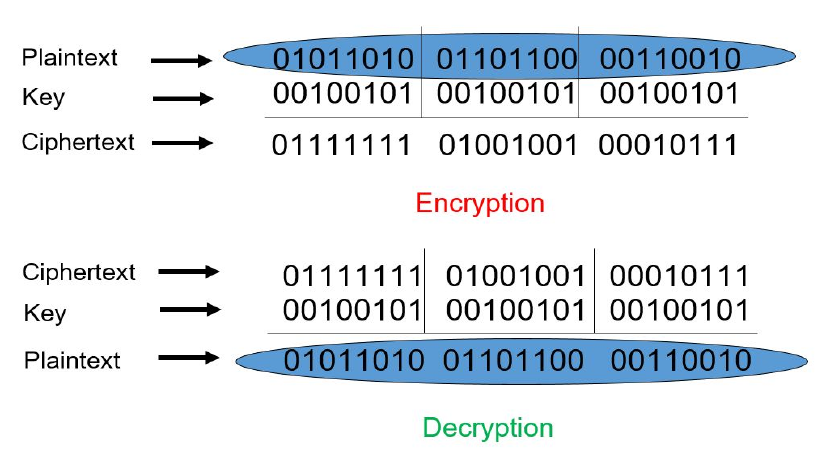
Symmetric Encryption #
Symmetric Encryption uses an identical key for both encrypting and decrypting the data.
Examples are DES (Data Encryption Standard) and Rijndael/AES

Symmetric encryption works by:
- Generating the keys: for example, 8-bit key = 00100101
- Taking the bit stream: for example, 010110100110110000110010
- XORing the bit stream with the key
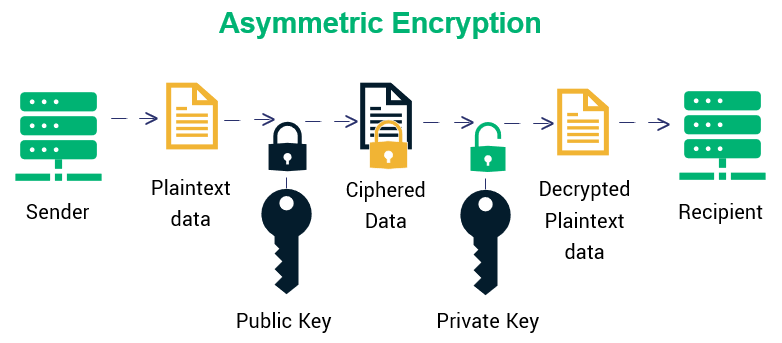
Asymmetric Encryption #
The key for encryption is different from the key for decryption.
Each user has a public key (P), and a private key (Q).
P(Q(M)) == M == Q(P(M))
Messages encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa.
Examples are RSA (Rivest, Shamir, and Adelman), and Diffie-Hellman algorithms
Hashing #
Hash functions allow a fixed length output to be generated from a variable length input.
Used commonly to verify the integrity of the data:
- A duplicated copy is the exact same as the original
- The data has not been compromised (integrity)
Popular hashing algorithms include: MD5 (Message Digest 5), SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm), SHA-2, etc.
Digital Signatures #
Used to verifies the messages, and that it belongs to the holder of the public/private key pair.
Appends a string of characters to a message (hash) for authentication and integrity check.
Works similar to a handwritten signature, but gives a greater reliability for identification than the signature on a document.