1. Introduction #
Data, Info, Knowledge, Wisdom #
Data is a collection of points with no discernible meaning.
Information is data in context.
Knowledge is information that has been assimilated in the mind.
Wisdom is the application of knowledge.
What is a Database? #
A database is a shared, integrated computer structure that houses:
- End user data (raw facts)
- Metadata (data about data)
Database Systems #
A database system consists of:
- Data (the database)
- Software
- Hardware
- Users
Database systems allow users to Store, Update, Retrieve, Organise, and Protect their data.
Database Users #
- End users: Use the database system to achieve some goal
- Application developers: Write software to allow end users to interface with the database system
- Database Administrator (DBA): Creates or modifies the schema, and designs and manages the database system
- Database systems programmer: Writes the database software itself
Uses of Databases #
- Businesses: Inventory, order processing, payroll, accounting, shipping
- Education: Educational institutions use databases to keep track of students, grades, transfers, transcripts, and other student data
- Non-Profits: Many charities and other non-profit groups use a database to store details of donations, volunteers, hours served in the community, clients helped, and other information related to the organisation
- Household and Family Management: Many people use databases to keep track of family birthdays, bills and expenses in the home, addresses of friends and relatives, and DVD collections
Each time you make a purchase and the sales clerk asks for your address or email, your information is kept and stored on a customer database. These collections of data are used to send mailings of special offers, discounts, and other deals.
Database Management Systems (DBMS) #
A DBMS is a collection of programs that manages database structure and cotnrols access to data.
A DBMS allows:
- Data to be shared among multiple applications or users
- Data management to be more efficient and effective
Advantages of s DBMS #
A DBMS solves many of the problems encountered in data management:
- Improved data sharing
- Improved data security
- Better data integration
- Minimised data inconsistency
- Improved data access
- Improved decision making
- Increased end-user productivity
File Based Systems #
- Data is stored in files
- Each file has a specific format
- Programs that use those files depend on knowledge about that format
- Disadvantages:
- No standards
- Data duplication
- Data dependence
- Inconsistent data
- Inflexibility
- Limited data sharing
- No way to generate ad-hoc queries
- No provision of security, recovery, concurrency, etc.
Data Models #
A data model is a collection of concepts for describing data.
A schema is a description of a particular collection of data, using a given data model.
The relational model of data is the most widely used model today:
- Relation: The main concept, basically a table with rows and columns
- Scheme: Every relation has a schema, which describes the columns, or fields
Levels of Abstraction #
Schemas are defined using Data Definition Language (DDL), data is modified/queries using Data Manipulation Language (DML).
- Views descrbe how users see the data
- Conceptual schema defines a logical structure
- Physical schema describes the files and indices used
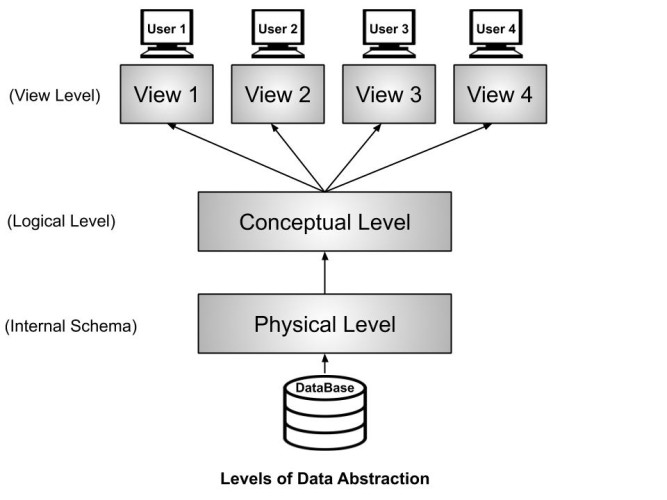
View Level or External Schema #
- Tells us how the data should be shown to the user
- Different users will have a different view according to the authorisation they have
- Different views increase the security of the system
Conceptual Level or Logical Level #
- Tells us how the data is actually stored and structured
- The data could be stored using different data models
- How the tables are related to each other
- The conceptual level creates a blueprint of the data
Physical Level or Internal Schema #
- Tells us where the data is actually stored
- It tells us the actual location of the data that is being stored by the user
- The Database Adminsitrators (DBA) decide:
- which data should be kept at which particular disk drive
- how the data has to be fragmented, where it has to be stored, etc.
- if the data has to be centralised or distributed
Types of Data Models #
- Hierachial Model
- Network Model
- Relational Model
- Object-oriented Data Model
- Entity-relationship Model
- NoSQL