2. IAS Computer #
Overview #
John von Neumann came up with the stored-program concept, where the instructions are read from part of memory rather than being input manually.
Von Neumann and his colleagues designed a new stored-program computer, knwon as the IAS computer.
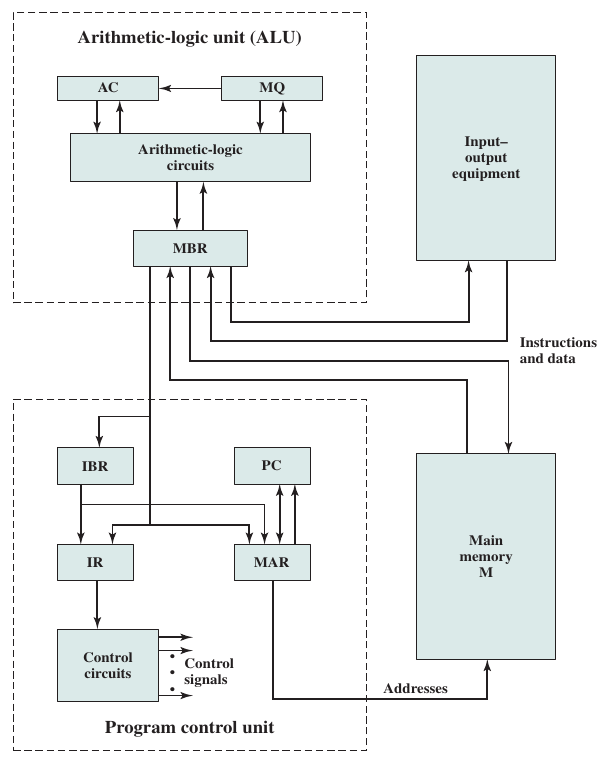
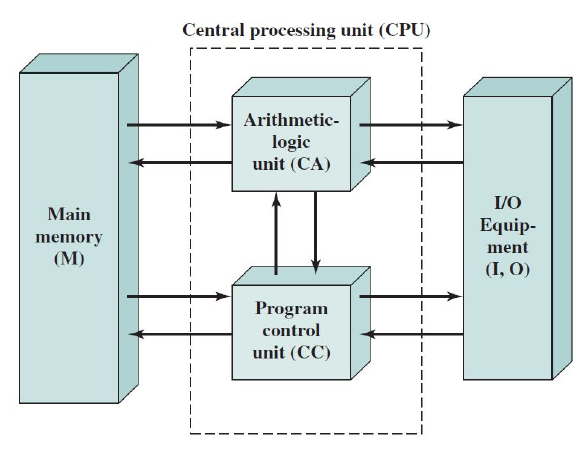
The general structure of the IAS computer consists of:
- Main Memory: Stores both data and instructions
- Arithmetic Logic Unit: Capable of operating on binary data
- Control Unit: Interprets the instructions and memory and causes them to be executed
- Input/Output: Equipment operated by the control unit
Memory Structure #
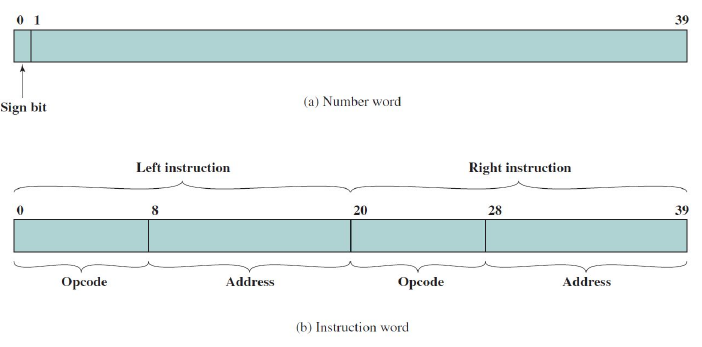
The memory of the IAS consists of:
- 1000 storage locations, called words
- Each word is 40 bits each
A word can either be a number word or an instruction word.
Registers #
The ALU contains the following storage locations, called registers:
- Memory Buffer Register (MBR): Contains a word to be stored or retrieved from memory or sent or retrieved from the I/O unit
- Memory Address Register (MAR): Specifies the address in memory of the word to be written or read into the MBR
- Instruction Register (IR): Contains the 8-bit opcode instruction being executed
- Instruction Buffer Register (IBR): Holds temporarily the right-hand instruction from a word in memory
- Program Counter (PC): Contains the address of the next instruction pair to be fetched from memory
- Accumulator (AC) and Multiplier Quotient (MQ): Used to hold temporarily operands and results of ALU operations.