1. Computer Structure and Function #
Architecture and Organisation #
Computer Architecture refers to the attributes that are directly visible to the programmer, and have an impact on the logical execution of a program.
- For example, the instruction set, and the number of bits required to represent various data types.
Computer Organisation refers to the operational units and their interconnections that realise the architectural specifications.
- For example, control signals, interfaces between the computer and peripherals, and the memory technology used.
An example is that it is an architectural decision whether a computer will have a divide instruction. It is an organisational decision whether it’ll be implemented in its own division unit or not.
Structure and Function #
Computer Structure refers to the way in which the components are interrelated.
Computer Function refers to the operation of each individual component as part of the structure.
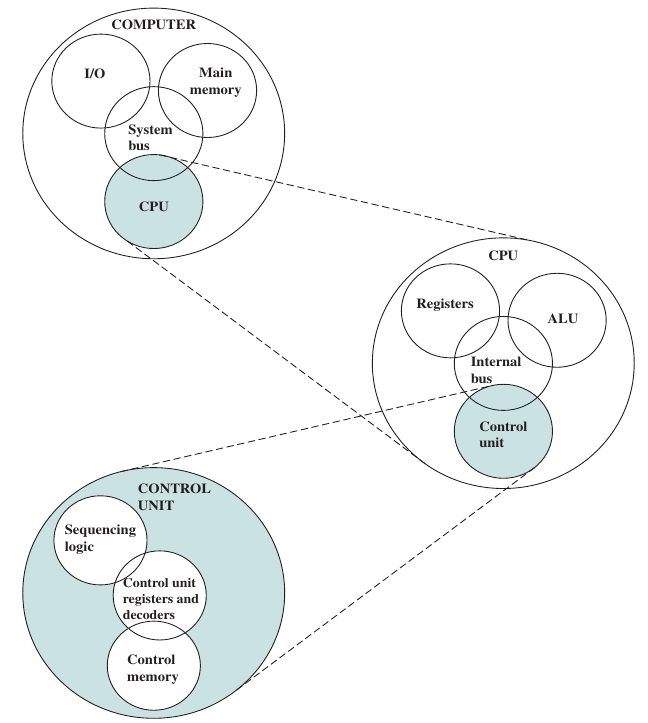
Structure #
There are four main structural components:
- Central processing unit (CPU)
- Main memory
- I/O
- System interconnection
The CPU contains the following sub-components:
- Control unit
- Arithmetic and logic unit (ALU)
- Registers
- CPU interconnection
The control unit contains the following sub-components:
- Sequencing logic
- Control unit registers and decoders
- Control memory
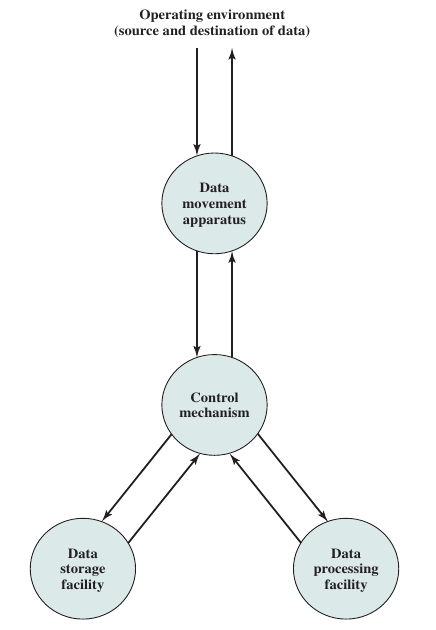
Function #
A computer can perform four basic functions:
- Data processing
- Data storage
- Data movement
- Data control