5. Computer Memory Systems #
Memory #
Computer Memory is where the computer stores or remembers data (in binary).
Memory stores information temporarily or permanently and provides the CPU with its instructions.
Key Characteristics #
- Location:
- Internal (e.g. processor registers, main memory, cache)
- External (e.g. optical disks, magnetic disks, tapes)
- Capacity:
- Number of words
- Number of bytes
- Unit of Transfer (the number of bits read out of or written into memory at a time):
- Bits (main mnemory)
- Word
- Block
- Access Method:
- Sequential access (linear sequence) - Tape units
- Direct access - Disk units
- Random access - Main memory, Cache systems
- Associative access - Cache systems
- Performance:
- Access time (latency)
- Cycle time
- Transfer rate (1/cycle time)
- Physical Type:
- Semiconductor
- Magnetic
- Optical
- Magneto-optical
- Physical Characteristics:
- Volatile/non-volatile
- Erasable/non-erasable
Memory Hierarchy #
- Greater Capacity -> Lower Cost per unit
- Greater Capacity -> Slower Access Time
- Faster Access Time -> Greater Cost
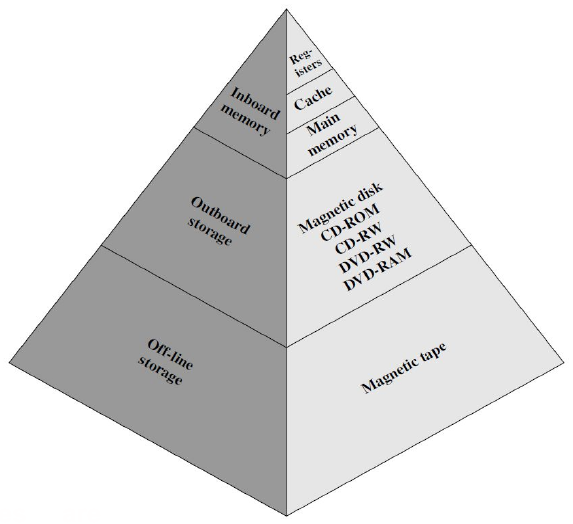
As the level goes down:
- Decreasing cost per bit
- Increasing capacity
- Increasing access time
- Decreasing frequency of access of the memory by processor
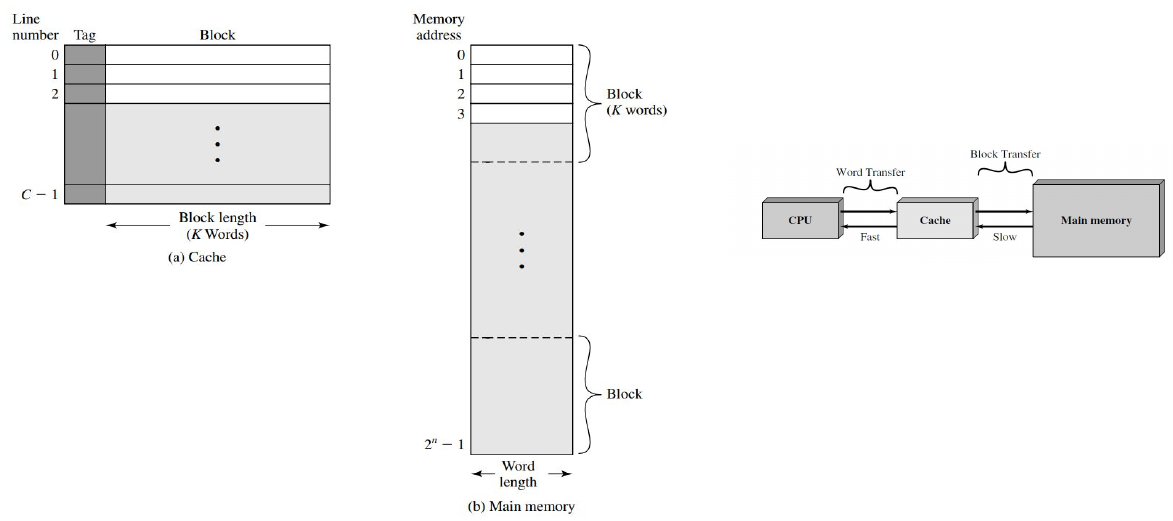
Cache Memory #
- Concept:
- Combine fast and expensive memory with less expensive and lower speed
- Cache contains a copy of portions of memory
- Multiple levels of cache organisation